The Term Used to Describe Dna Dependent Dna Polymerization Is
DNA-dependent DNA polymerase It helps in the polymerisation catalyses and regularises the whole process of DNA replication with the support of other enzymes. B Pol I has a slower polymerization rate than Pol III.

Rna Directed Dna Polymerase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Base-Pairing Underlies DNA Replication and DNA Repair.

. DNA-dependent RNA polymerization Rd. RNA viruses have RNA genomes which can also be either double-stranded dsRNA or single-stranded ssRNA. Coli DNA polymerases Pol I and Pol III.
The position of gDNA sequence is underlined. A Pol I has a 3 to 5 exonuclease and DNA Pol III does not. Transcription proteins assemble at the promoter to form the basal transcription apparatus and begin synthesis of RNA.
DNA Polymerase Definition DNA Polymerases are a group of enzymes that catalyse the synthesis of DNA during replication The main function of DNA polymerases is to duplicate the DNA content of a cell during cell division. The DNA continues the synthesis of DNA until the end when the strand ends the polymerization stops. Both of them perform polymerization activity from 5 to 3.
Display boostrap support above 50 under branch labels option is shown 1000 replicates. DNA polymerase will add the free DNA nucleotides using complementary base pairing A-T and C-G to the 3 end of the primer this will allow the. RNA polymerase moves along the DNA template in a 3 to 5 direction unwinding the DNA and synthesizing RNA in a 5 to 3 direction.
DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritance. Since the DNA-dependent CeNA polymerization and the CeNA-dependent DNA polymerization is possible to a limited extend we suggest CeNA as an ideal candidate to use in. The DNA-dependent RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and catalyses the polymerization in the 5 to 3 direction on the template strand.
Deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates are the substrate as well as the energy provider for the replication process. But RNA polymerase is different. Transcription Unit is a stretch of a DNA transcribed into an RNA molecule.
These enzymes are essential for DNA replication and usually work in groups to create two identical DNA duplexes from a single original DNA duplex. Answer DNA replication machinery and enzymes process of replication requires a set of catalysts enzymes 1 The main enzyme is DNA dependent DNA polymerase as it uses DNA as template to catalyses the polymerization of deoxynucleotides. PDF Background Single molecule measurements of DNA polymerization kinetics provide a sensitive means to detect both secondary structures in.
DNA polymerase 1 also known as Kornberg enzyme has only 1 subunit made up of 928 amino View the full answer. Branches were transformed to proportional option. As L1 RT lacks RNase H activity intact L1 mRNA in the heteroduplex apparently serves a stabilization factor during generation of first strand DNA and later is either cleaved by cellular RNases or displaced by L1 RT during second strand DNA synthesis.
Hence synthesizes entire chromosomal DNA. DNA viruses replicate their genomes using DNA-dependent DNA polymerases also called DNA polymerases and transcribe mRNA using DNA-dependent RNA polymerases also called RNA polymerases. A DNA polymerase is a member of a family of enzymes that catalyze the synthesis of DNA molecules from nucleoside triphosphates the molecular precursors of DNA.
The process of DNA polymerization is dehydration synthesis catalyzed by a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase. The polymerization through RNA polymerase is terminated when finds the stop codon or termination codon on the nucleic acid strand. D Pol I is a single subunit while Pol III is a multisubunit protein.
Once it reaches the terminator sequence the process terminates and the newly synthesised RNA strand is released. DNA dependent DNA polymerase It helps in the polymerization and catalyzes and regularises the whole process of DNA replication with the support of other enzymes. Presently geneticists use the term genetic polymorphism to describe the inter-individual functionally silent differences in DNA sequence that make each human genome unique.
This is essential for cell division during growth and repair of damaged tissues while it also ensures that each of the new cells receives its own. In molecular biology DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA polymerase or DNA dependent DNA polymerase 1 and 3 both are found in eubacteria such as Ecoli.
Tissue-distribution of mutations is displayed by color code. C Pol I is less processive than Pol III. As discussed briefly in Chapter 1 DNA templating is the process in which the nucleotide sequence of a DNA strand or selected portions of a DNA strand is copied by complementary base-pairing A with T and G with C into a complementary DNA sequence This process entails the recognition of each nucleotide in the.
In simple words the term polymorphism was originally used to describe variations in shape and form that distinguish normal individuals within a species from each other. They do so by adding nucleotides at 3-OH group of the growing DNA strand. It is a part of DNA replication but does not constitute all of the reactions that are required for in vivo DNA replication.
During this process DNA polymerase reads the existing. Which statement does NOT accurately describe a difference between E. RNA dependent synthesis of RNA and DNA Pages 996 1022 Difficulty 2 Compare from BIOCHEM 1234 at Kenyatta University.
The DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity of L1 RT described here directs efficient polymerization on L1 DNA. Among them DNA-dependent DNA polymerase is the main enzyme. Describe what happens at each stage.
2 Replicat View the full answer.

Dna Polymerase Iii Holoenzyme An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Okazaki Fragments An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

So Many Dna Polymerases So Little Time Goldbio

Rna Directed Dna Polymerase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
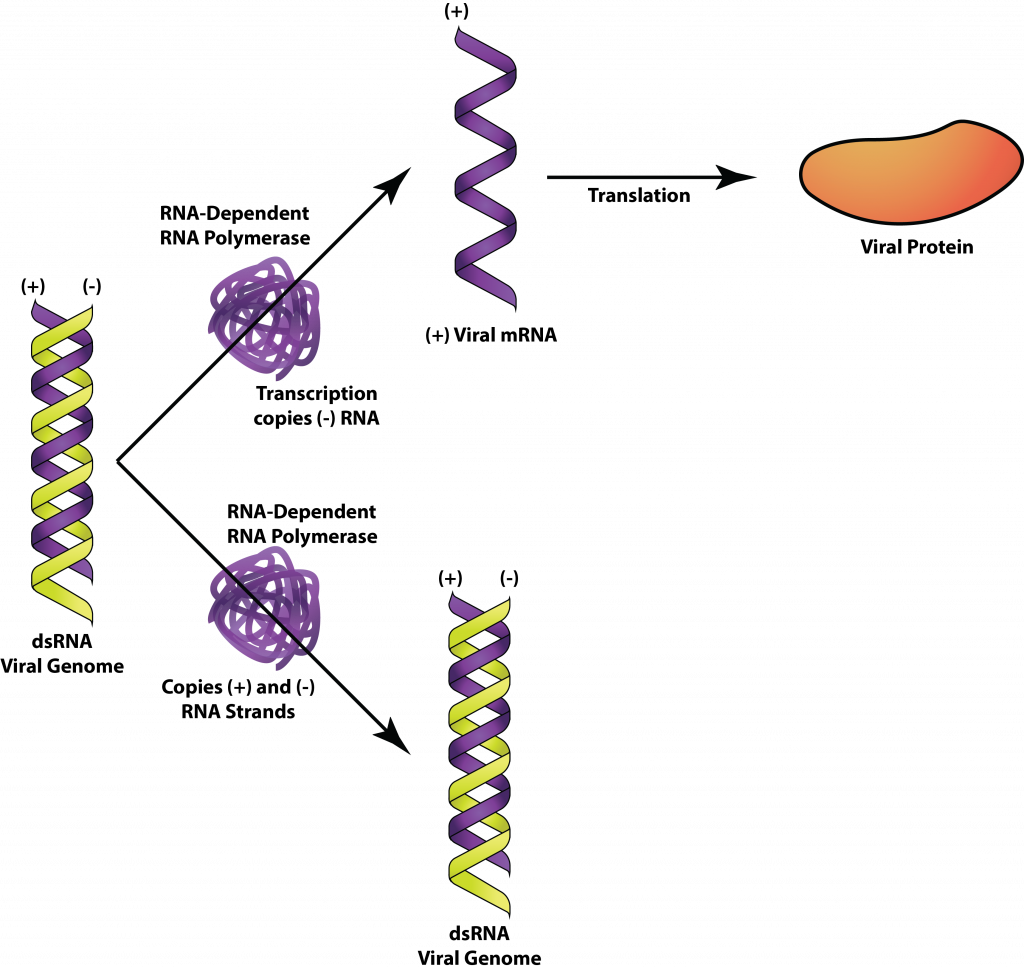
The Viruses General Microbiology
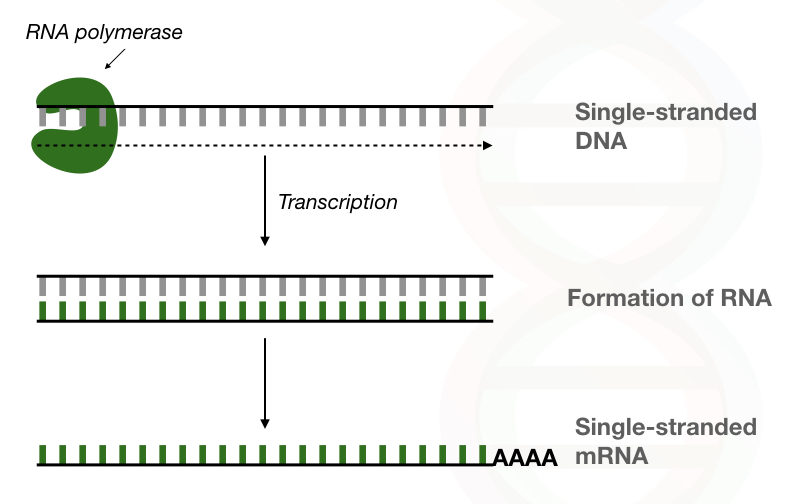
Comparison Between Dna Polymerase Vs Rna Polymerase
Chapter 9 Dna Replication Chemistry
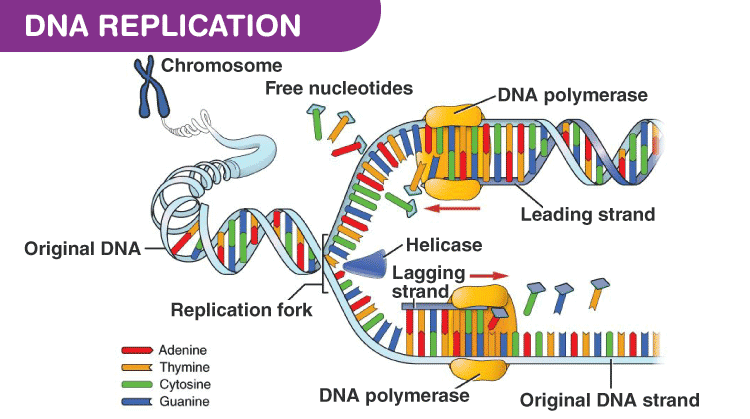
Dna Polymerase Structure Types And Functions

Rna Polymerase I An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
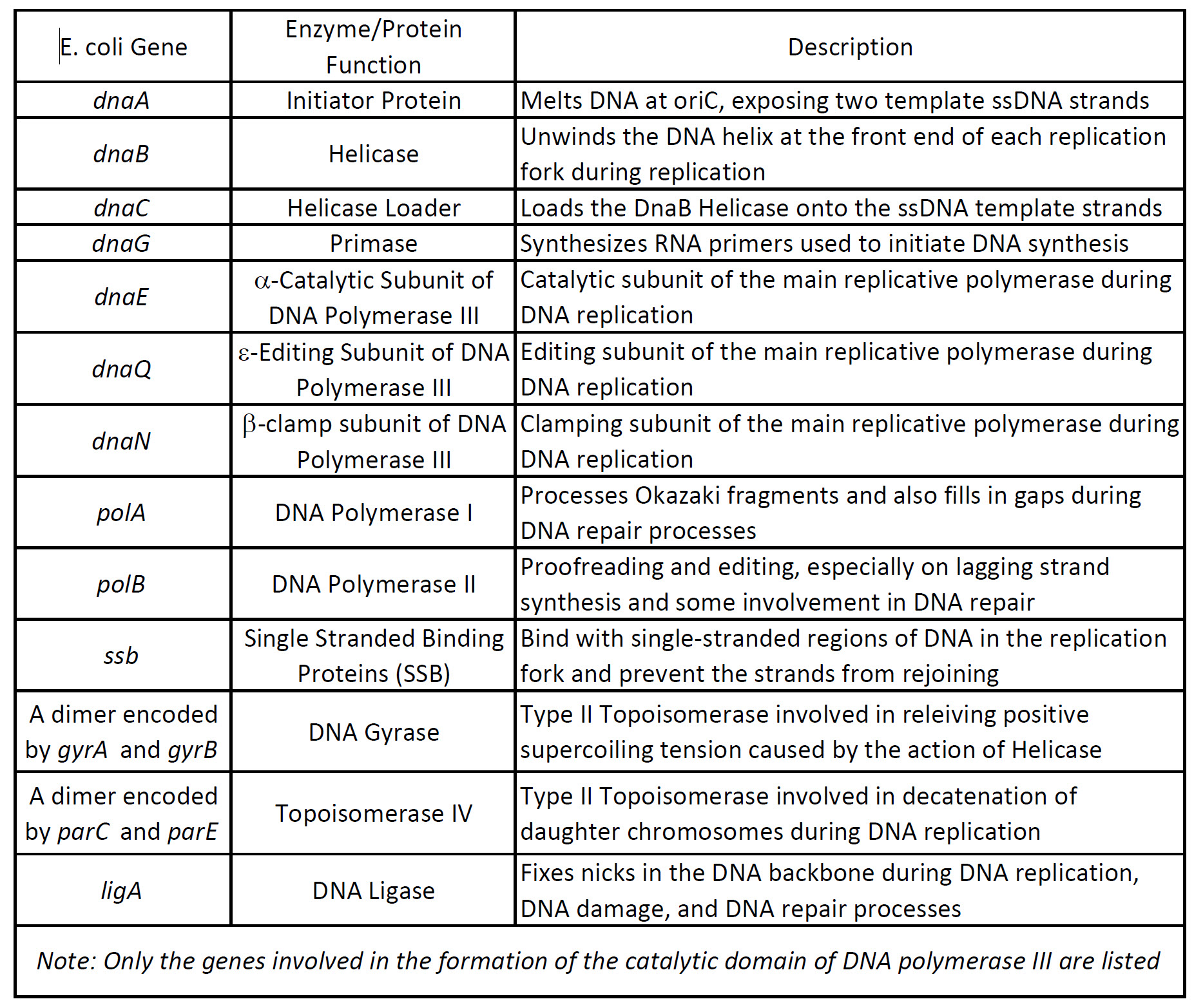
Chapter 9 Dna Replication Chemistry

Dna Directed Dna Polymerase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Chapter 9 Dna Replication Chemistry

Dna Polymerase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

The Biotechnology Revolution Pcr And Cloning Expressed Genes Learn Science At Scitable

Dna Polymerase An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

Dna Polymerases Structural Diversity And Common Mechanisms Journal Of Biological Chemistry

22 The Viruses Biology Libretexts
Difference Between Dna And Rna Polymerase Definition Replication Transcription Process

Comments
Post a Comment